Redux is a predictable state container for JavaScript apps.
官网第一句就很全面的介绍了redux。一个可预测的状态管理工具。redux 是如何做到的呢?
- 单一的数据源 (states)
- states是只读且不可变化的 (每次改变返回新值)
- 通过纯函数改变states (reducer, 无副作用, 相同的输入就有相同的输出)
- 改变states方式具有可描述性且单一 (action)
数据流
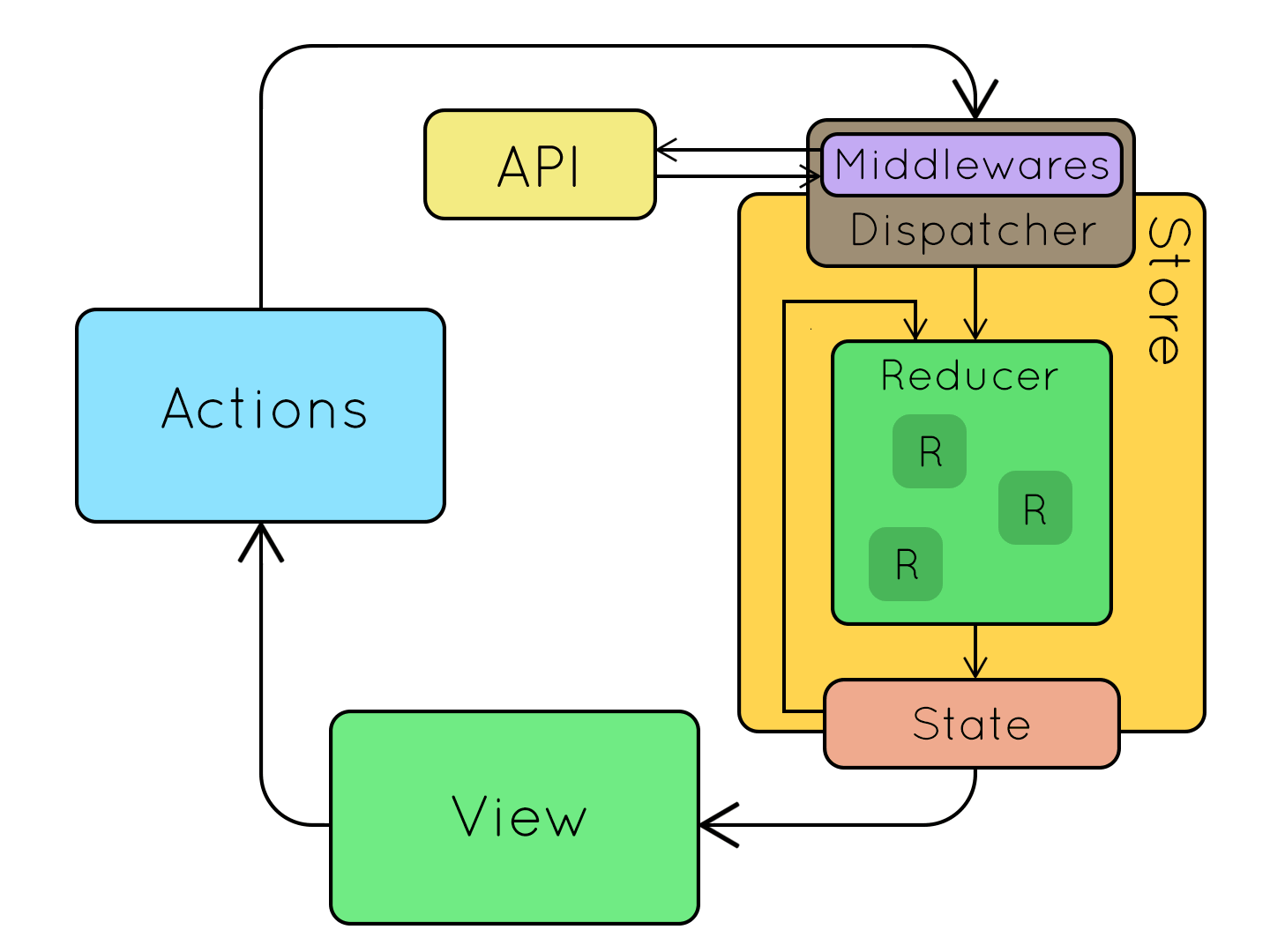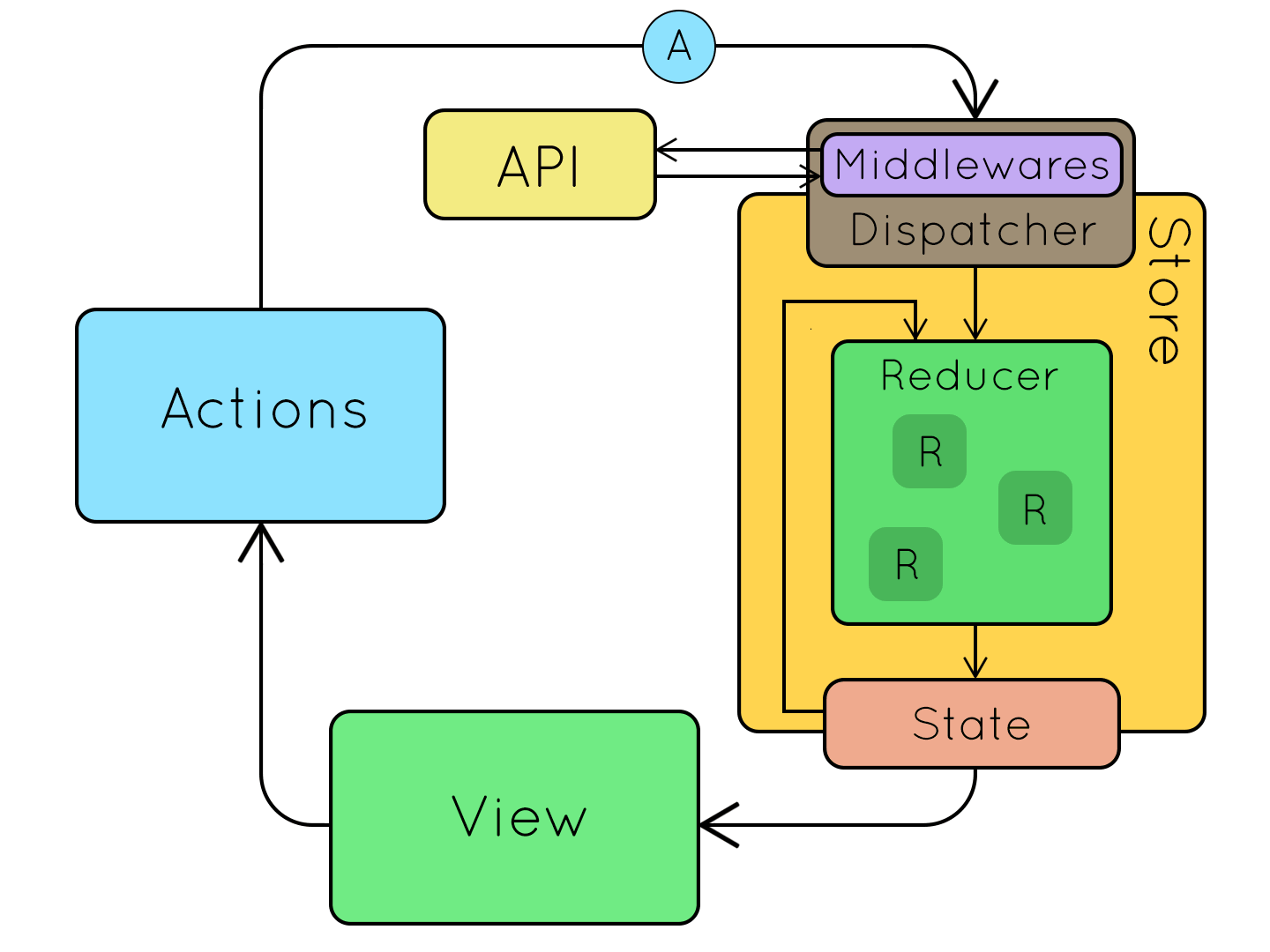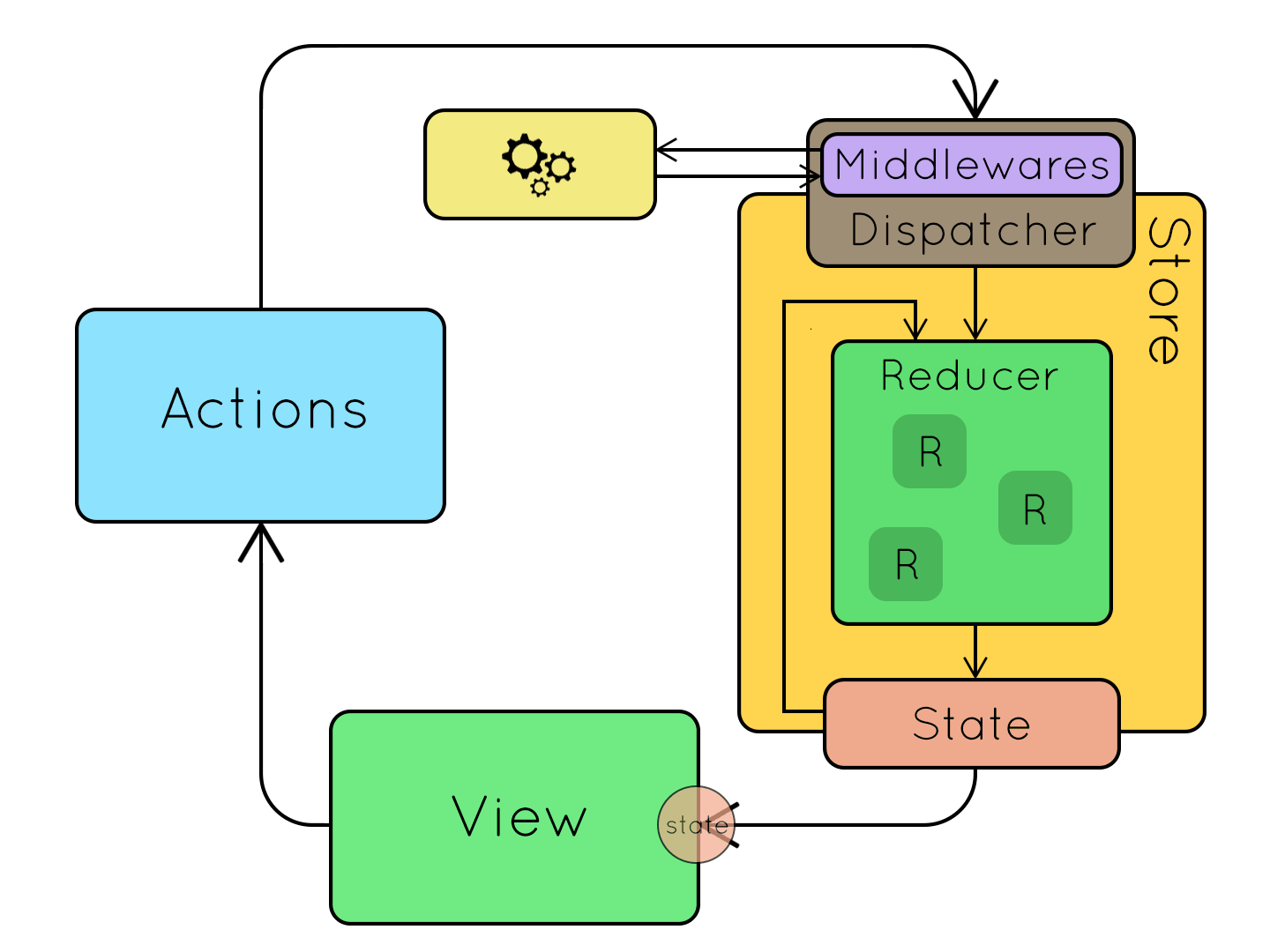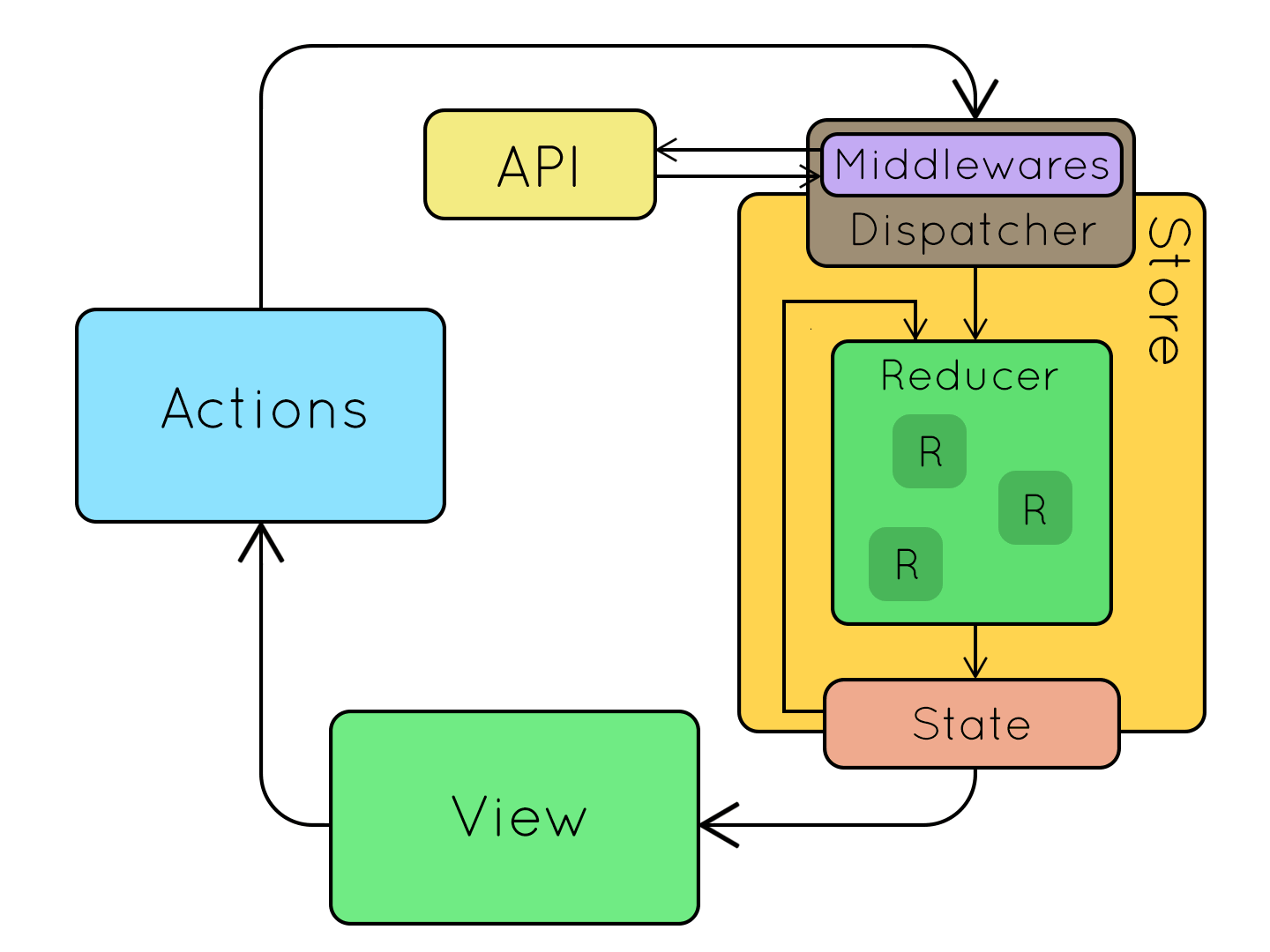
这个大家都很熟悉了吧,就不再讲了
源码解读
createStore
func createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) -> ({ dispatch, subscribe, getState, replaceReducer,[$$observable]: observable })1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78export default function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
// preloadedState 可以不传,确定真实的参数
if (typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'undefined') {
enhancer = preloadedState
preloadedState = undefined
}
if (typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') {
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)
}
let currentReducer = reducer
let currentState = preloadedState
let currentListeners = []
let nextListeners = currentListeners
let isDispatching = false
function ensureCanMutateNextListeners() {
if (nextListeners === currentListeners) {
nextListeners = currentListeners.slice()
}
}
function getState() {
return currentState
}
function subscribe(listener) {
let isSubscribed = true
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
nextListeners.push(listener)
return function unsubscribe() {
isSubscribed = false
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
const index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener)
nextListeners.splice(index, 1)
}
}
function dispatch(action) {
try {
isDispatching = true
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action)
} finally {
isDispatching = false
}
const listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners)
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
const listener = listeners[i]
listener()
}
return action
}
function replaceReducer(nextReducer) {
currentReducer = nextReducer
dispatch({ type: ActionTypes.REPLACE })
}
function observable() {
//...
}
dispatch({ type: ActionTypes.INIT })
return {
dispatch,
subscribe,
getState,
replaceReducer,
[$$observable]: observable,
}
}
为了篇幅减少些,上面的代码我删掉了部分错误检查。其实都很好理解,就有一点需要注意一下,为什么要用两个变量(currentListeners,nextListeners)来储存listener。这是因为redux允许在subscirbe中执行unsubscribe。
例如:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9const unsubscribe1 = store.subscribe(() => {
unsubscribe1()
})
const unsubscribe2 = store.subscribe(() => {
unsubscribe2()
})
dispatch(unknownAction);
如果不缓存dispatch的listener的话 那么在dispatch里循环listeners时就会有问题。
另外也可以发现,如果你绑定了多个subscribe函数,即使在第一个subscription里执行了所有的unSubscribe,subscription还是会全部执行一遍
另外 observable 是为了和其他一些observable库配合使用,当目前为止还没用过。
applyMiddleware
用法
1 | const logger = ({ getState }) => next => action => { |
源码
1 | export default function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) { |
可以compose原因是middle模式统一:store => next => action => {}
在执行完 const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))之后
chainItem: next => action => {} 本质是 接收一个dispatch,再返回一个合成的dispatch
bindActionCreators
用法
bindActionCreators({ actionCreator1, actionCreator2, …}, dispatch) => ({ boundAction1, boundAction2, … })
源码
1 | // 返回 boundAction |
combineReducers
由于redux仅有一个store,所以当项目复杂的时候,数据需要分类,这时就会用到此函数。作用是将多个分开的reducers合并。
原型:(reducer1,reducer2, reducer3,…) => combinedReducer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73export default function combineReducers(reducers) {
const reducerKeys = Object.keys(reducers)
const finalReducers = {}
// 遍历检查 reducer 不应该为 undefined
for (let i = 0; i < reducerKeys.length; i++) {
const key = reducerKeys[i]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (typeof reducers[key] === 'undefined') {
warning(`No reducer provided for key "${key}"`)
}
}
if (typeof reducers[key] === 'function') {
finalReducers[key] = reducers[key]
}
}
const finalReducerKeys = Object.keys(finalReducers)
let unexpectedKeyCache
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
unexpectedKeyCache = {}
}
let shapeAssertionError
try {
// 检查 reducer 必须设置初始值,不可以返回 undefined
assertReducerShape(finalReducers)
} catch (e) {
shapeAssertionError = e
}
// combinedReducer
return function combination(state = {}, action) {
if (shapeAssertionError) {
throw shapeAssertionError
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 检查 state 是否合法,例如state必须是对象、state应该有相对应的reducer等
// 使用了combineRudcer之后,state就是对象了,原来的state都放在了相对应的key下面
// 例如:combineReducers({ todos: reducer1, todoType: reducer2 });
// store 变成了 { todos: todoState, todoType: todoTypeState };
const warningMessage = getUnexpectedStateShapeWarningMessage(
state,
finalReducers,
action,
unexpectedKeyCache
)
if (warningMessage) {
warning(warningMessage)
}
}
let hasChanged = false
const nextState = {}
// 将action分发给每个reducer, 如果该改变就返回新的。
// 否则返回旧值,类似于你在每个reduer中的做法。
for (let i = 0; i < finalReducerKeys.length; i++) {
const key = finalReducerKeys[i]
const reducer = finalReducers[key]
const previousStateForKey = state[key]
const nextStateForKey = reducer(previousStateForKey, action)
if (typeof nextStateForKey === 'undefined') {
const errorMessage = getUndefinedStateErrorMessage(key, action)
throw new Error(errorMessage)
}
nextState[key] = nextStateForKey
hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey
}
return hasChanged ? nextState : state
}
}
总结
redux源码还是比较好理解的,记住reducer一定要保证是纯函数。这对于测试和与其他的库配合至关重要。例如 react-redux。
感兴趣的朋友可以看看我的react-redux源码分析
- react-redux源码分析及实现原型
- react-redux源码分析及实现原型(下)
下周会给大家带来redux-saga这个中间件源码解读,感兴趣的请关注~
参考阅读
https://blog.gisspan.com/2017/02/Redux-Vs-MVC,-Why-and-How.html